Abstract
Teratological spores and pollen are widespread in sediments that record the Permian-Triassic mass extinction. The malformations are thought to be the result of extreme environmental conditions at that time, but the mutagenic agents and the precise timing of the events remain unclear. We examined the abundance of teratological sporomorphs and metal concentrations in a Permian-Triassic tropical peatland succession of southwestern China. We find a significant peak of spore tetrads of lycopsid plants (as much as 19% of all sporomorphs) coeval with increases in Cu and Hg concentrations above the main terrestrial extinction interval, which marks the loss of Permian Gigantopteris forests, increased wildfire activity, and the disappearance of coal beds. Thus, in tropical peatlands, mutagenesis affected only surviving plants. Mutagenesis was likely caused by metal toxicity, linked to increased Hg and Cu loading, but was not itself a direct cause of the terrestrial crisis.
Fighure 1: Lithological column and organic carbon isotopes (δ13Corg) (A), total organic carbon (TOC) (B), Hg concentration and Hg/Al and Hg/ TOC ratios (C), Cu concentration and Cu/Al and Cu/TOC ratios (D), and tetrad frequency as proportion of total spores (E) for ZK4703 borehole, southwestern China (25.54151°N, 104.28994°E), and photographs of normal (F) and tetrad (G) Aratrisporites (scale bar is 20 μm). Log shows lithologies (C—coal; M—mudrocks; Si—siltstone; Sa—sandstone) with approximate representation of color. Gray bar shows onset of negative carbon isotope excursion (CIE) coupled with loss of Gigantopteris flora. Yellow bar shows enrichment in heavy metals and tetrad spike. Data for organic carbon isotopes, TOC, Hg concentration, and Hg/TOC ratios are from Chu et al (2020).
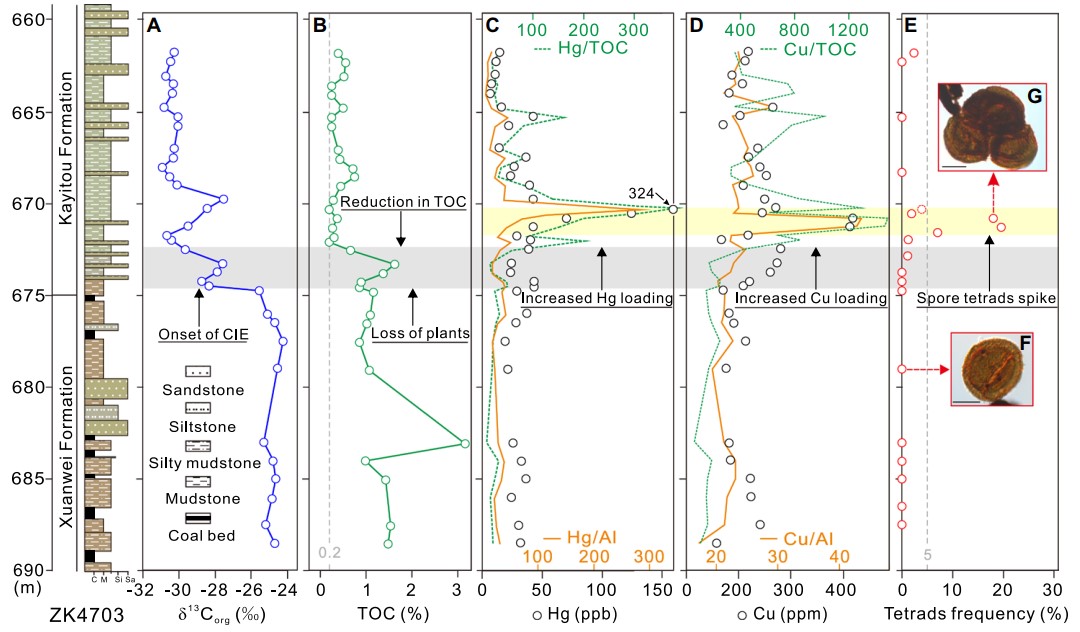
Figure 2: Selection of normal and tetrad spores from sample ZK-41 of ZK4703 borehole, southwestern China (25.54151°N, 104.28994°E). (A–C) Aratrisporites spp. (normal). (D) Lapposisporites echinatus (dyad or one half of tetrad). (E–G) Unseparated tetrads of Lapposisporites echinatus. Scale bar is 20 μm.
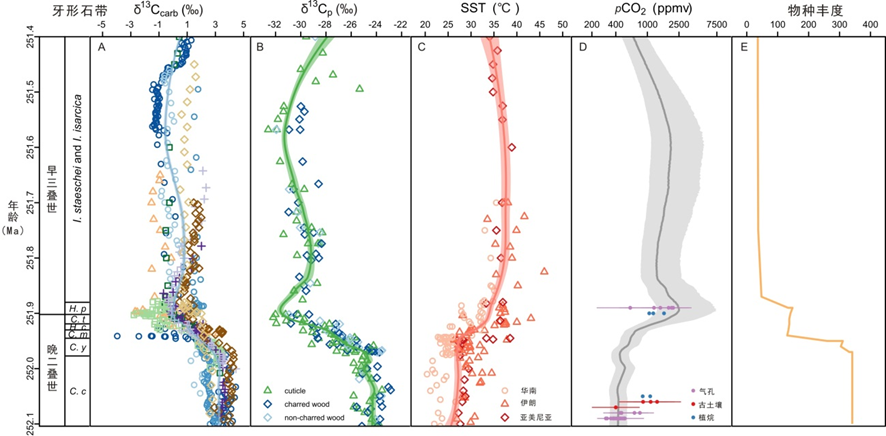
Title:Wu, Y.Y., Chu, D.L.*, Tong, J., Song, H.J., Dal Corso, J., Wignall, P.B., Song, H.Y., Du, Y. and Cui, Y.*, 2021. Six-fold increase of atmospheric pCO2 during the Permian–Triassic mass extinction. Nature Communications 12: 2137.
Doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22298-7
Title: Chu, D.L.*, Dal Corso, J., Shu, W.C., Song, H.J., Wignall, P.B., Grasby, S.E., van de Schootbrugge, B., Zong, K.Q., Wu, Y.Y. and Tong, J.N., 2021. Metal-induced stress in survivor plants following the end-Permian collapse of land ecosystems. Geology.
Doi: 10.1130/G48333.1